Intro
The previous post showed how to install WSL in order to use ROS on my classes. With Ubuntu setted up in my WSL configuration, I am now able to proceed to install and test ROS. This process will be described using Ubuntu 20.04.
What is ROS
Following it's own documentation (ROS Wiki), ROS is:
ROS (Robot Operating System) provides libraries and tools to help software developers create robot applications. It provides hardware abstraction, device drivers, libraries, visualizers, message-passing, package management, and more. ROS is licensed under an open source, BSD license.
How to install it
- Open a terminal connected to WSL.
- Use
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'. to accept software from packages.ros.org. - Following with:
sudo apt install curlecurl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ros/rosdistro/master/ros.asc | sudo apt-key add -. - Update apt packages and install ros:
`sudo apt updateesudo apt install ros-noetic-desktop-full. - Use
source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bashin every bash intended to run ROS. - Install dependencies to be able to build packages:
sudo apt install python3-rosdep python3-rosinstall python3-rosinstall-generator python3-wstool build-essential. - Finally use
sudo rosdep init | rosdep update.
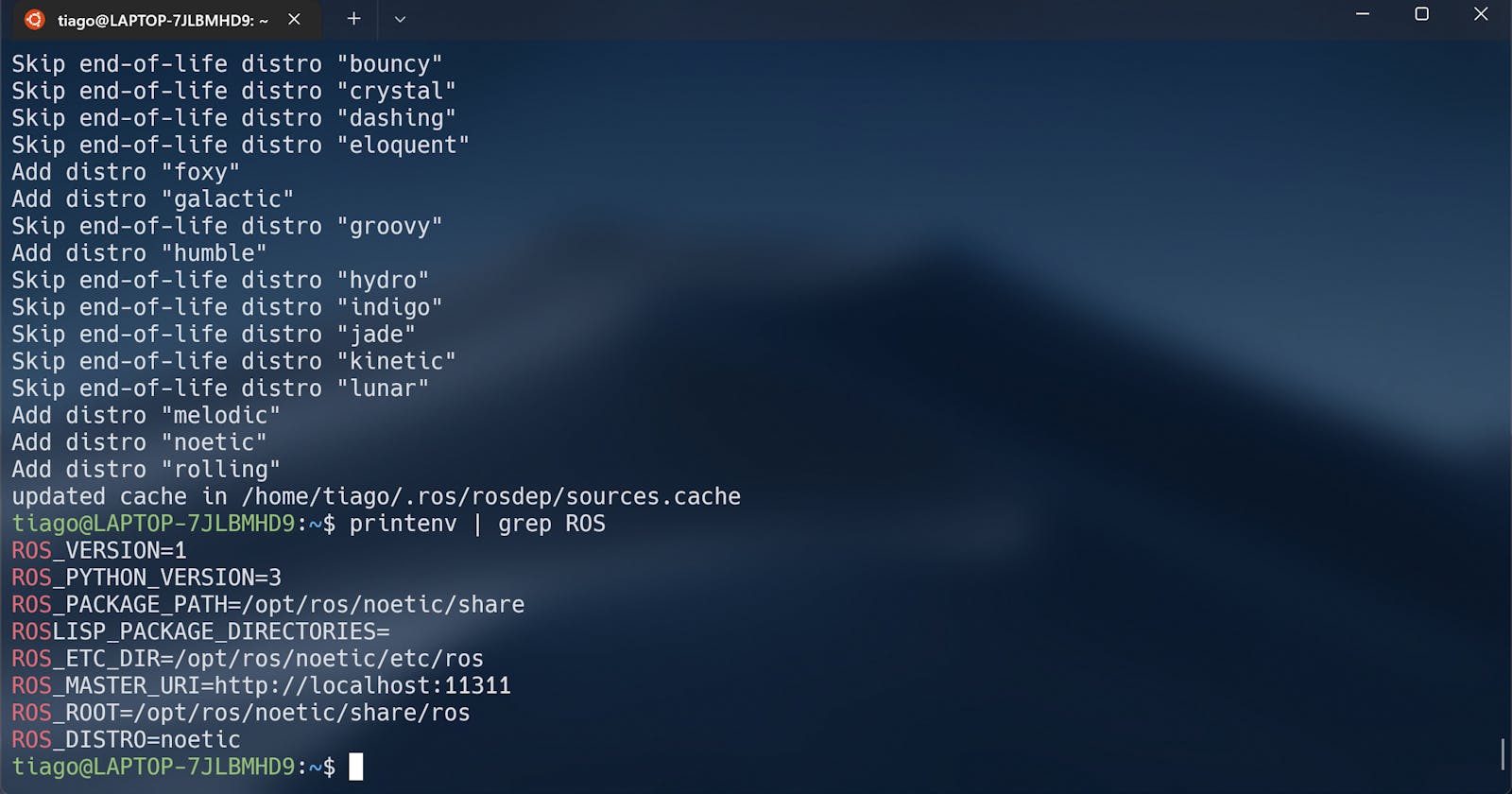
It's possible to validate the installation with printenv | grep ROS
Hot to add a gui for applications running on WSL
While using WSL, there isn't a GUI for applications. To fix that it's possible to setup a X-server application, that allows for GUI forwarding. I recommend VcXsrv Windows X Server.
Run the installer and use default options. Just mind to uncheck "Native opengl" and check "Disable access control". Go ahead and save your configuration, for faster boot up.
To finish run echo 'export DISPLAY={ip_address}:0.0' >> ~/.bashrc and source it to the bash source ~/.bashrc., and replace ip_address for your current ip, you need to update this when your main ipv4 changes.